Basic Linux Tutorial for Beginners

What is Linux
Linux is an operating system created by Linus Torvalds. It’s a free and open-source that powers about 80% of the servers. There are several distribution of the Linux OS as there are different distribution of the Windows OS, some distributions are;
- Ubuntu (Kinda the popular one)
- Debian
- Fedora
- Kali Linux (Used by Cyber-Security analyst mostly for Penetration Testing)
These different distros are all Linux distribution, just that it’s has been modified by adding more applications and performance to execute specific functions. When a computer is not running a windows OS, there’s a 80% probability it is running one of the Linux distribution. Also, with the help of Virtual Machine (Virtualization), a computer running windows OS can still run any Linux distro.
The Linux Shell or Terminal
The terminal is an Command Line Interface (CLI) that receives commands as user input and pass it on to the OS for processing. All distros of the Linux OS comes as a Graphical User Interface (GUI). In this tutorial, we will be discussing some basic/popular/useful shell commands and their functions. Below is what Linux CLI look like.

To execute commands on the Linux CLI, it has to be typed in lower case. In rare instance do you have to type in upper case to execute a command. If you need to know more about the commands we will be talking about today, you can use the manual page or the help page of each command. To access the manual page of any command just type
man commandName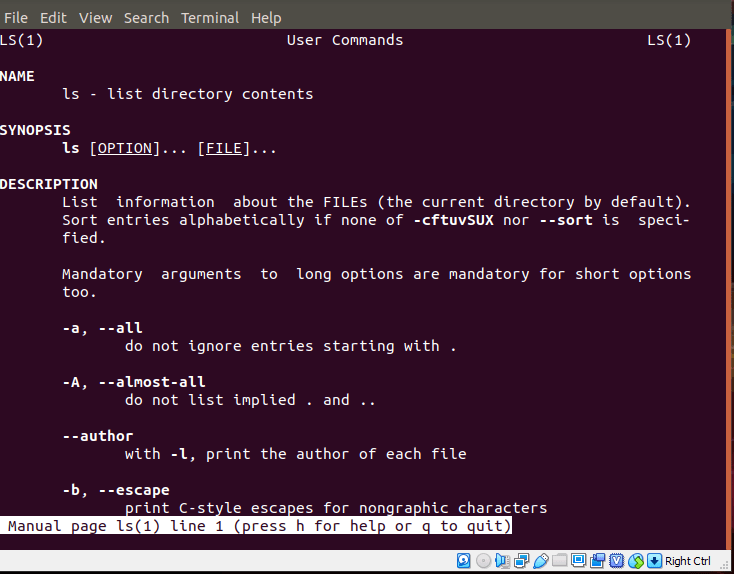
And to access the help page of any command, just type
commandName -- help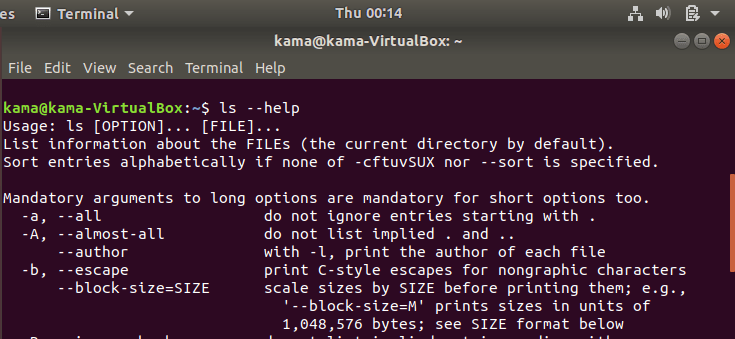
Without wasting any time, the first command we would look at is the ls.
- ls (list), is a command used to list the content of present directory/folder you are in. To use the ls command just type
ls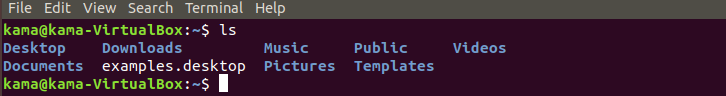
However it can be combined with different arguments such as
ls -l ( to list all properties, including permissions of folders In a directory )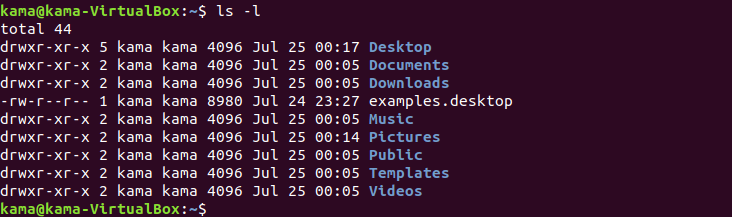
ls -a ( to list all hidden file/folders)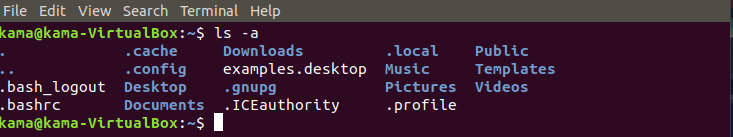
ls * ( to list all folders and subfolders)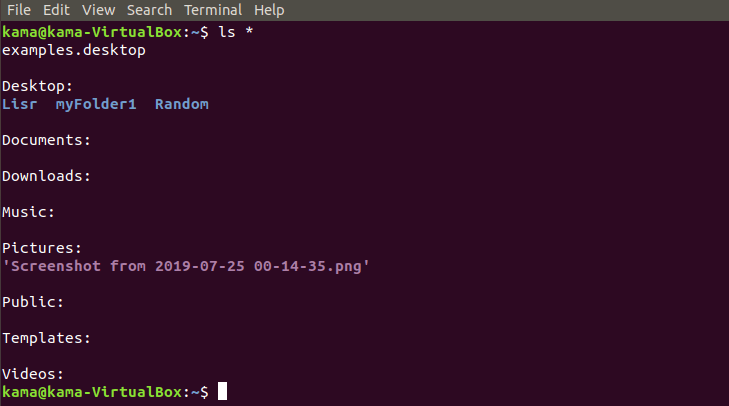
ls -r ( to list all files in reverse order)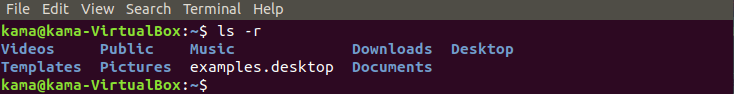
ls -l
ls ~ (to list all file in the home directory)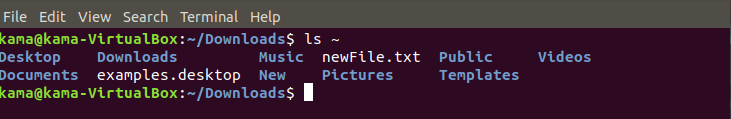
- cd (change directory), is used in the Linux CLI to change your current directory (folder/sub folders ) into another directory, as long as you have access to the directory. You can also change directory into another completely different directory as long as you know the full path to it. To picture this; on your home screen, you have different folders; such as Documents, Downloads, Desktop and so on. If you wish see what’s inside the Desktop folder, you double click it. This is basically what the cd is doing, however through the CLI. To use the cd command just type
cd file path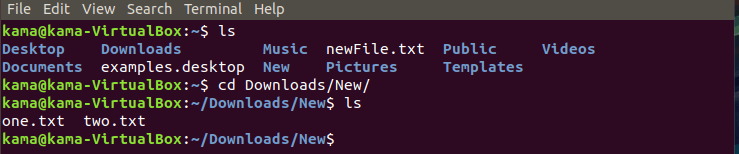
cd folder-name
cd .. ( to go back one step at your current directory)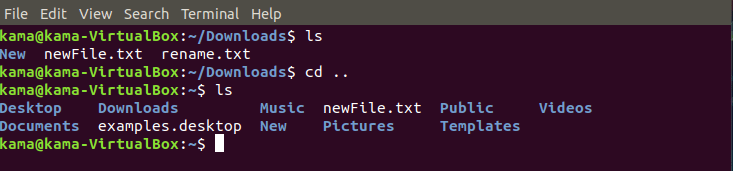
cd ~ ( to go back to the head folder of the directory your are)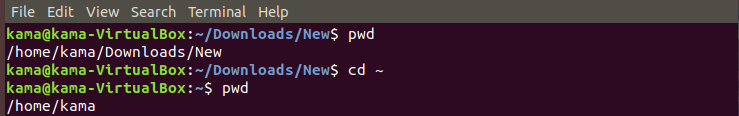
- rm (remove), is a Linux command used to delete files/folder. To use the rm command just type
rm filename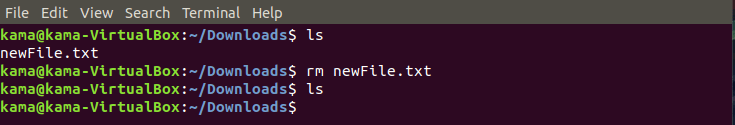
and to remove a folder just type
rm -R folder-name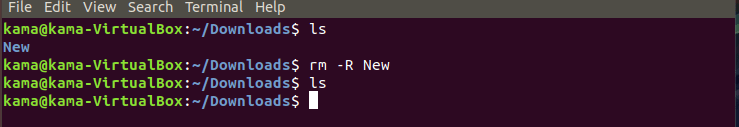
- cp (copy), is a Linux command used to copy a file/folder from a location to another location To use the cp command just type
cp filename /destination_directory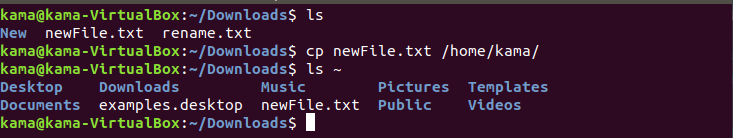
and to copy a folder
cp -R filename /destination_directory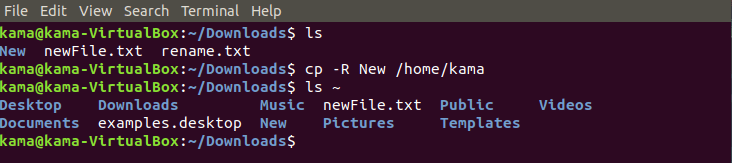
- mv (move), command can be used to move and rename a file . To use the mv command type
mv filename /destination_directory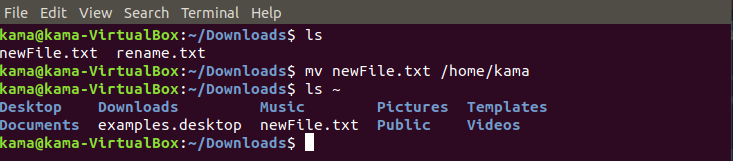
and to rename a file type
mv filename newfilename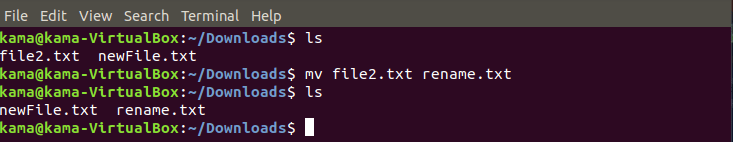
- nano is a Linux command that act as an text editor in the CLI. nano command can be used to view,edit and create a new file. To view/edit a file type
nano filename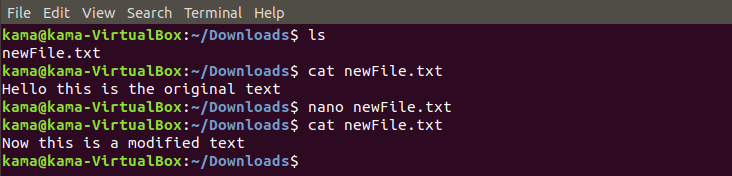
and to create file that doesn’t exit yet type
nano filename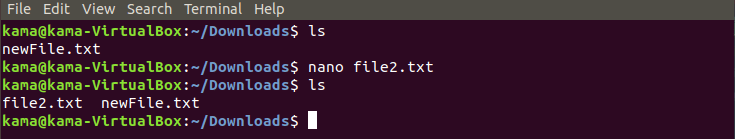
- touch is a Linux command used to create a new file . To use the touch command type
touch filename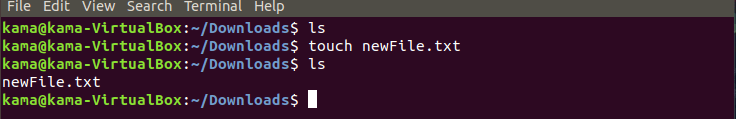
- mkdir (make directory), is a command used to create folders in Linux terminal . To use the mkdir command, type
mkdir foldername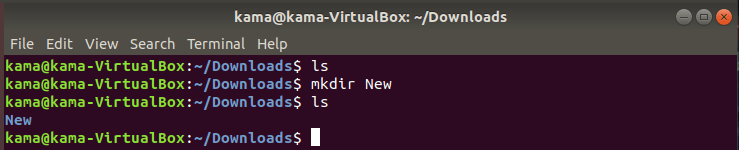
- clear is a Linux command used to clear the screen Linux terminal. To use the clear command, type
clear
- history, is a Linux command used to list all the command you’ve executed in the past To use the history command, type
history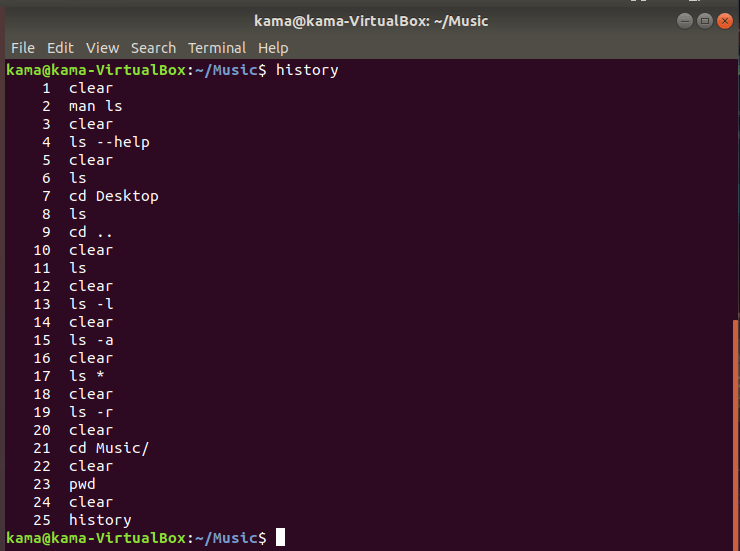
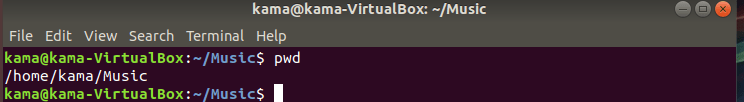
- pwd (print working directory), is a command used to display the path to the current directory you are working on. The pwd will display the current directory you are working on. To use the pwd command, type
pwd